Catalytic converter components:
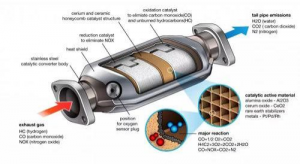
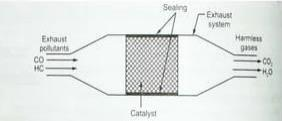
The catalytic converter consists of a catalyst made of platinum, palladium, rhodium, or a mixture of these two materials. A catalyst is any material that accelerates a chemical reaction without changing its properties. The catalyst is coated on a block of ceramic formed with holes (in the shape of a honeycomb) or on small ceramic pellets. The catalyst is housed in a stainless steel housing designed to be heat resistant
In the next lines, we will clarifying its types
Types of catalytic converters
Single oxidative catalytic converter
A catalytic converter that uses a catalyst consisting of a block of ceramics is called a unified type converter, and when small ceramic pellets are used it is called a catalytic converter with pellets. This is known as a single-layer conversion system, and the engine works in the case ofthis system with a poor mixture and air is pumped
before in the converter, the hydrocarbons HC and carbon monoxide CO are oxidized to water vapor H2O and carbon dioxide CO2. The disadvantage of this type is that the nitrogen oxides (NOx) remain as they are and are not affected practically.
2 way catalytic converter
It contains two layers; one of which contains the reducing catalysts to reduce nitrogen oxides NOx, and the second layer contains the oxidizing catalysts and works to reduce each of the hydrocarbons HC and carbon monoxide CO, respectively. In this system, the exhaust gases first pass through the reduction bed, which converts nitrogen oxide (NOx) into ammonia (NH3) and other compounds. As for the second layer, it is a secondary air pump between the two layers, so the hydrocarbons HC and carbon monoxide CO are almost completely oxidized into H2O water vapor and carbon dioxide.
In addition, the engine works in the presence of this system with a rich mixture, which means an increase in fuel consumption, and this is one of the defects of the system. The second defect is when the ammonia is partially re-oxidized in the oxidized layer to NO. Therefore, the total reduction percentage of nitrogen oxide is limited to about 70% to 80%
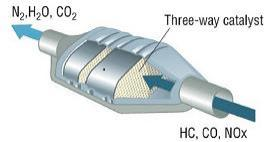
3 way catalytic converter
This system contains one layer of catalyst, which has three paths. In this type of converters, hydrocarbons HC, carbon monoxide CO, and nitrogen oxides NOx are reduced with a high degree of accuracy because of the use of an electronic circuit that senses the percentage of oxygen in the exhaust, which makes the control unit handle the mixing ratio to suit different operating conditions
Important note:
Some cars use a small catalytic converter that sits close to the engine and heats up quickly at start-up (when the engine and main catalytic converter are cold) to reduce emissions during the engine warm-up period. A small catalytic converter is used with a larger main converter.
Post time: Jan-18-2023